近日,我院长聘副教授罗杭与北京外国语大学国际组织学院讲师李博轩合作在The British Journal of Politics and International Relations(SSCI JCR Q1 in two categories, Political Science and International Relations)在线发表论文International Network Analysis based on Big Data: The Case of Economic Cooperation among the G20。The British Journal of Politics and International Relations是英国政治学会(Political Studies Association)会刊。
论文摘要:
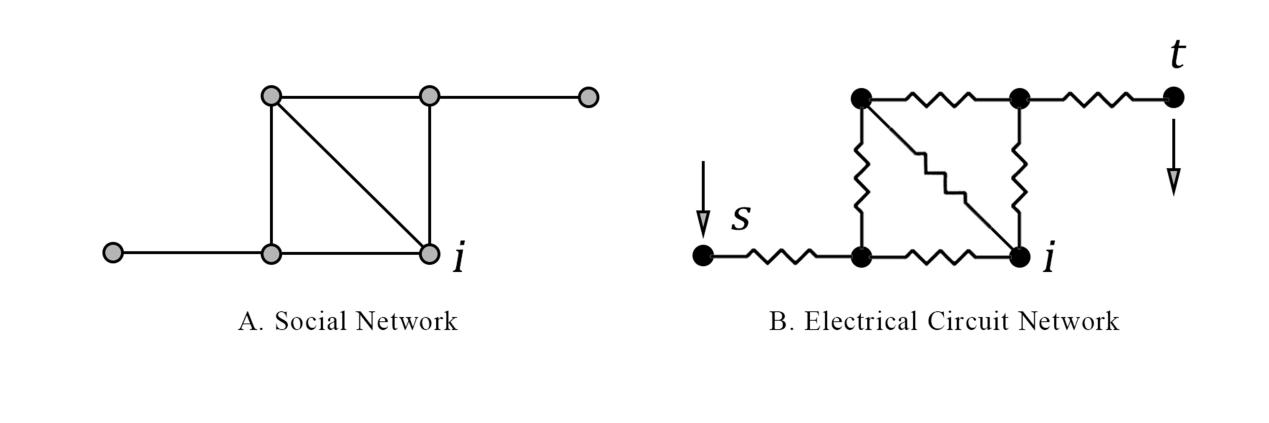
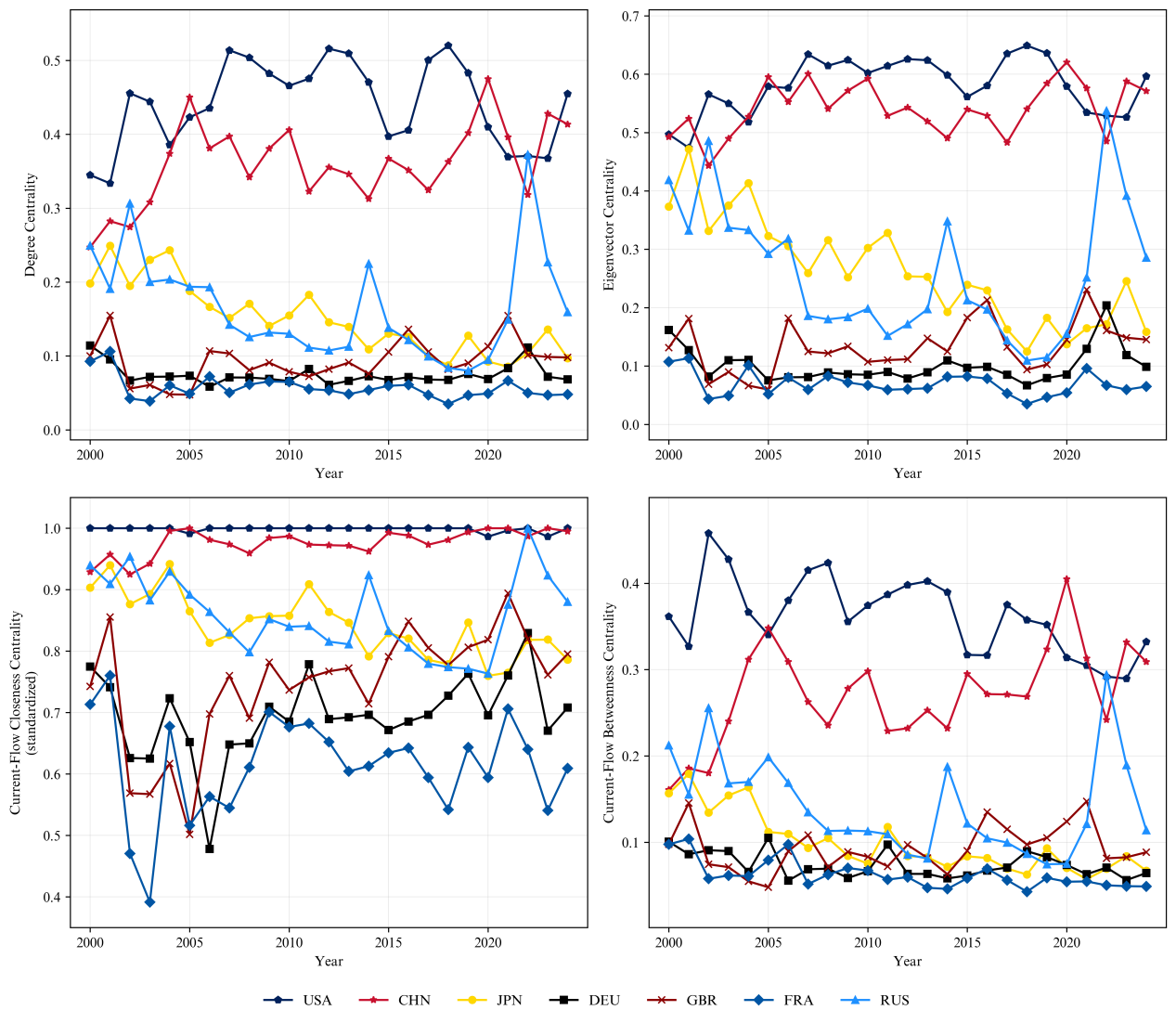
How the structure of the international economic cooperation network among the G20 countries has evolved over the past quarter century, and what are the roles and power levels of different countries in the network? We collect big data on economic cooperation events among the G20 countries from 2000 to 2024, and divide the 25 years into four periods using structure changepoint detection algorithms to separately construct international economic cooperation networks. We calculate and compare the multifaceted characteristics of the G20 economic cooperation network and trade network based on network analysis. At the macrolevel of network structure, we find that even when trade relations among the G20 countries became closer, economic cooperation among them became more distant. At the mesolevel of group classification, the result of community detection and the disparity of edge weight of the G20 economic cooperation network and trade network show clear but different regional characters. At the microlevel of power distribution, we measure and compare the power levels of the G20 countries in the economic cooperation network and their dynamics over time using weighted centrality indices based on current flow and random walks. By combining network analysis and event big data, we study economic interactions between countries in a unique approach that differs from traditional approaches employing trade volume or institutional data (e.g. free trade agreements).
过去四分之一世纪里,二十国集团(G20)成员国间的国际经济合作的网络结构如何演变?不同国家在该网络中扮演着怎样的角色,又拥有何种权力水平?在收集2000至2024年G20国家间经济合作事件大数据的基础上,运用结构变点检测算法将这25年划分为四个时期,分别构建国际经济合作网络。基于网络分析,计算并比较了G20经济合作网络与贸易网络的多维特征。在宏观网络结构层面,发现G20国家间贸易关系日益紧密的同时,经济合作却呈现疏离趋势。在中观群体分类层面,G20经济合作网络与贸易网络的社区发现结果以及边权重差异分析呈现出鲜明但不同的区域特征。在微观权力分布层面,运用基于电流模型和随机游走的加权中心性指标,测量并比较了G20国家在经济合作网络中的权力水平及其消长。通过结合网络分析与事件大数据,以区别于传统的使用贸易额或制度数据(如自由贸易协定)的研究路径,深入剖析国家间的经济互动关系。